| Classification | Water treatment agent |
| EINECS No | 215-477-2 |
| CAS No | 1327-41-9 |
| MF | Al2Cl(OH)5 |
| Purity | High purity |
| Content | 24-30% |
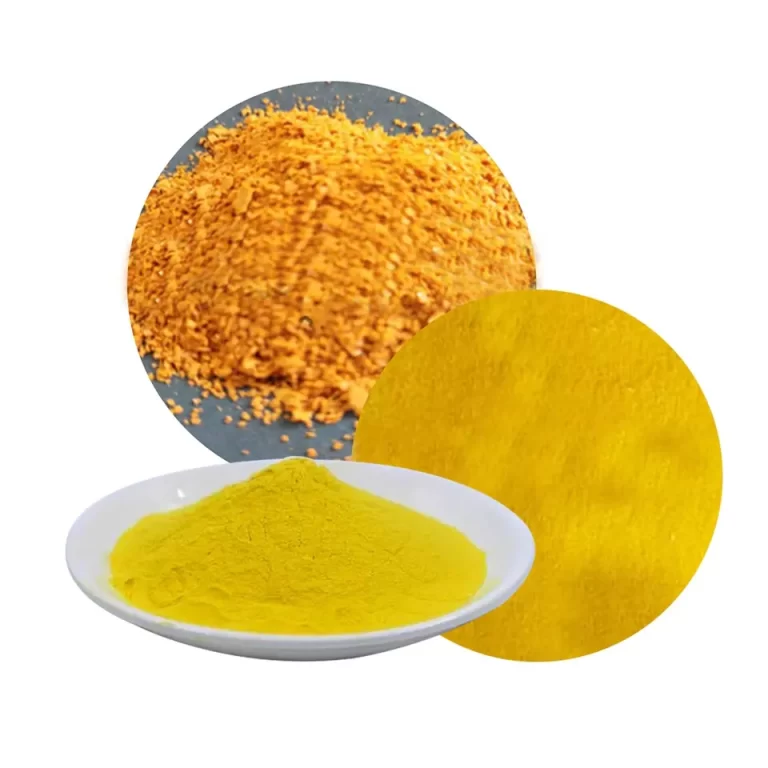
| Product appearance | Yellow granules |
Products Description
Printing and dyeing is a process of chemical treatment of textile materials (fibers, yarns and fabrics). The printing and dyeing industry is one of the industries that discharge a large amount of pollutants in China. A large amount of printing and dyeing wastewater is discharged every day, which will affect the environment. The pollution is serious and endangers human health.
The source and water quality characteristics of printing and dyeing wastewater:
Printing and dyeing wastewater mainly comes from various printing and dyeing processes. Typical printing and dyeing processes are divided into: desizing, refining, bleaching, mercerizing, dyeing, finishing, and drying finished products.
Dyeing wastewater can be divided into the following categories:
(1) Desizing wastewater: wastewater accounts for 15% of the total water volume, with high concentration of pollutants and a pH value of about 12. It contains various slurries, slurry hydrolysates (such as starch decomposing enzymes), caustic soda and various additives. Sizing-starch-based desizing wastewater has high COD and BOD values and good biodegradability; but desizing wastewater dominated by polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) has relatively low BOD and poor biodegradability.
(2) Smelting wastewater: large amount of water, alkaline pH value, high temperature, high pollutant concentration, brown.
(3) Bleaching wastewater: The amount of water is large, but the pollution is relatively light. It contains residual bleaching agent, a small amount of acetic acid, oxalic acid, sodium thiosulfate, etc.
(4) Mercerizing wastewater: it can be reused, so the amount of discharged water is small, containing caustic soda, sulfuric acid, acetic acid, etc., the concentration of caustic soda is 220-280g/L, which is relatively alkaline, but BOD, COD, and SS are low.
(5) Dyeing wastewater: large water volume, high chroma (400-600 times), water quality varies with the different dyes used, including slurry, dyes, auxiliaries, surfactants, etc., with complex and changeable ingredients. Generally, it is strongly alkaline and has poor biodegradability.
(6) Printing wastewater: The amount of water is large, it contains a lot of dyes, auxiliaries and slurries, the concentration of pollutants is high, the content of ammonia nitrogen is high, and BOD and COD are both high.
(7) Treatment of wastewater: The amount of water is small, containing resin, surfactant, oil, slurry, etc., and pollution is small.
| Index name | Index | |
| First Grade | ||
| Drinking water % | Non drinking water % | |
| alumina (AL2O3) mass fraction/%≥ | 28-30 | 27-29.0 |
| Basicity/% | 40-90 | 40-90 |
| density (20oC)/(g/cm3) ≥ | 1.12 | 1.12 |
| Mass fraction of water insolubles /% ≤ | 1.0 | 1.5 |
| PH(1% aqueous solution) | 3.5-5.0 | 3.5-5.0 |
| arsenic (As) mass fraction /% ≤ | 0.005 | 0.005 |
| lead (Pb) mass fraction /% ≤ | 0.001 | 0.003 |
| cadmium (Cd) mass fraction /% ≤ | 0.002 | 0.002 |
| mercury (Hg) mass fraction /% ≤ | 0.00001 | 0.00001 |
| Six valence chromium(Cr+6) mass fraction /% ≤ | 0.005 | 0.005 |


Q:Where does PAC apply to sewage treatment?
A:Decolorization, precipitation, air floatation, dehydration, coagulation.
Q:What type of medicament does PAM belong to? How many kinds of flocculation process? What type of medicament is PAC?
A:1. Flocculant or organic flocculant, settling agent
2. Air floatation, sedimentation and mud pressure.
3. Coagulant or inorganic coagulant
Package

About Us