| Classification | Water treatment agent |
| EINECS No | 215-477-2 |
| CAS No | 1327-41-9 |
| MF | Al2Cl(OH)5 |
| Purity | 24%-30% |
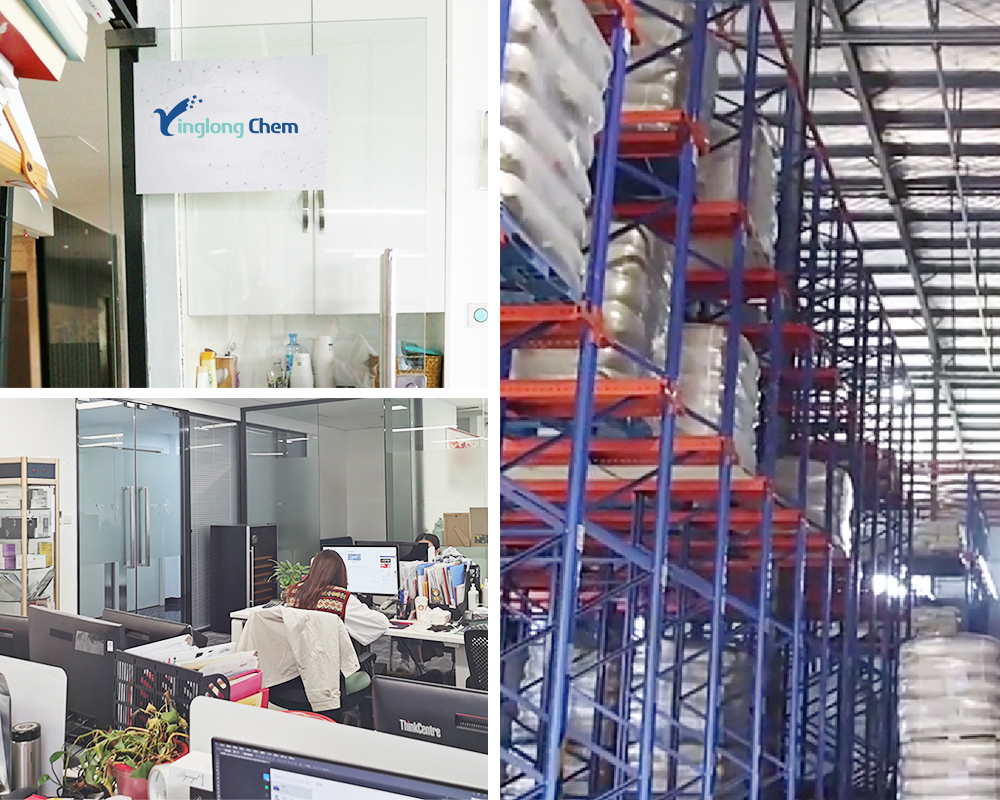
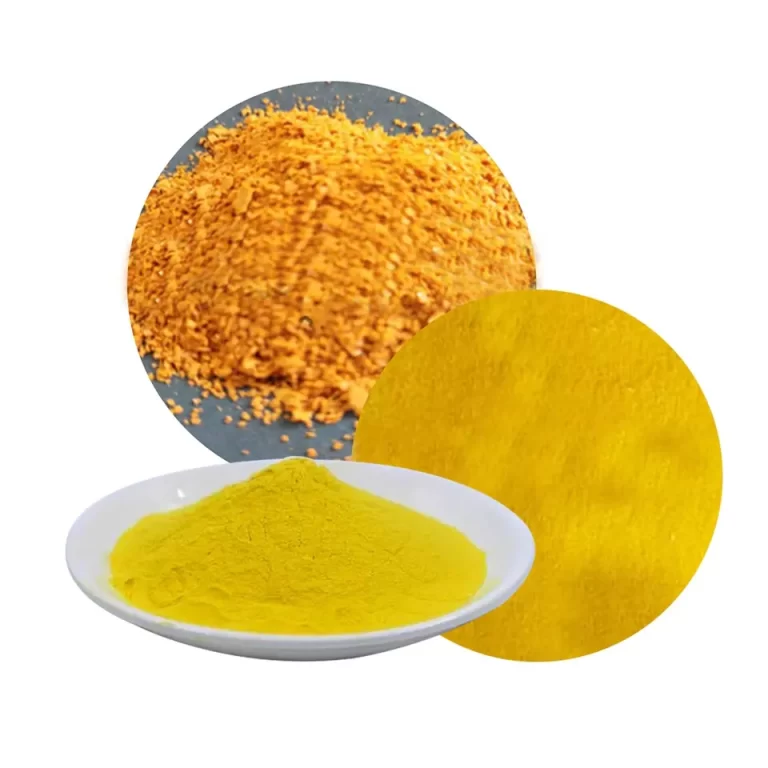
| Product appearance | Yellow to white powder |
Properties of polyaluminium chloride
1.Wide range of application and wide adaptability to water.
2.It is easy to form large alum flowers quickly and has good precipitability.
3.The water quality after purification is better than inorganic coagulant suchas aluminum sulfate, and the cost of water purification is 15-30% lower than that.
| Index name | index | |
| First Grade | ||
| Drinking water % | Non drinking water % | |
| alumina (AL2O3) mass fraction/%≥ | 28-30 | 27-29.0 |
| Basicity/% | 40-90 | 40-90 |
| density (20oC)/(g/cm3) ≥ | 1.12 | 1.12 |
| Mass fraction of water insolubles /% ≤ | 1.0 | 1.5 |
| PH(1% aqueous solution) | 3.5-5.0 | 3.5-5.0 |
| arsenic (As) mass fraction /% ≤ | 0.005 | 0.005 |
| lead (Pb) mass fraction /% ≤ | 0.001 | 0.003 |
| cadmium (Cd) mass fraction /% ≤ | 0.002 | 0.002 |
| mercury (Hg) mass fraction /% ≤ | 0.00001 | 0.00001 |
| Six valence chromium(Cr+6) mass fraction /% ≤ | 0.005 | 0.005 |


Q:Where does PAC apply to sewage treatment?
A:Decolorization, precipitation, air floatation, dehydration, coagulation.
Q:What type of medicament does PAM belong to? How many kinds of flocculation process? What type of medicament is PAC?
A:1. Flocculant or organic flocculant, settling agent
2. Air floatation, sedimentation and mud pressure.
3. Coagulant or inorganic coagulant
Package

About Us